
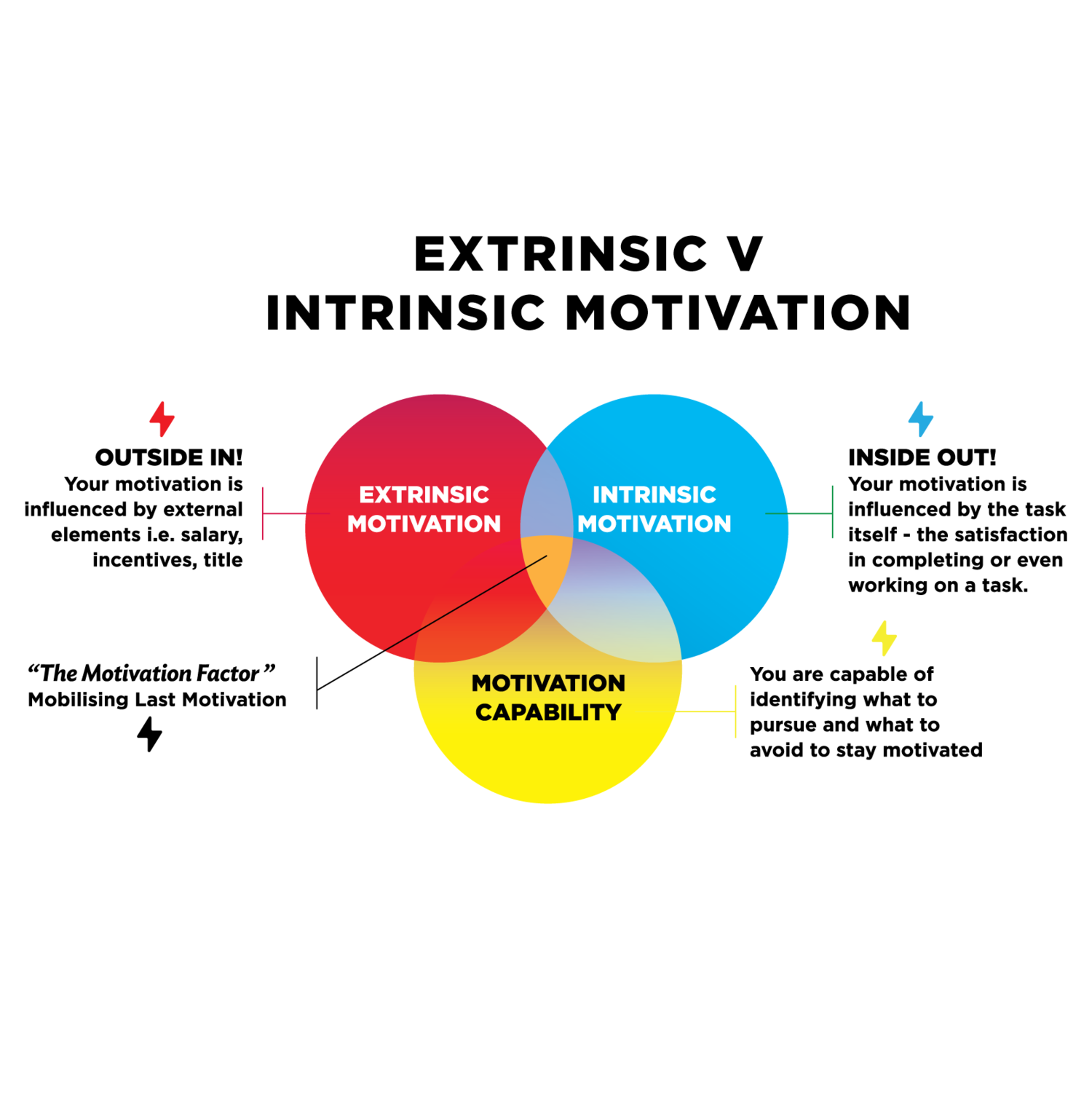
When motivating ourselves, and our children, to complete a task, it can be useful to remind ourselves of the power of intrinsic vs.
#Know extrinsic vs intrinsic motivation driver#
Even with extrinsic rewards, athletes who feel like they are in control of their behaviors, will be more satisfied and more likely to continue participating.Motivation is an interesting driver because what motivates someone may be completely different for someone else. The more athletes experience competence and success due to their own actions and skills, the great their intrinsic motivation. Work together with your athletes to set individual and team goals that are challenging and realistic. Recognize athletes’ specific contribution to practice or the team you will be positively informing athletes about their ability.

Give nonverbal and verbal positive reinforcement based on the specific behaviors of your athletes. Your behaviors, as a coach, can influence the intrinsic motivation of your athletes and helping athletes feel like they control their own behavior even with the presence of extrinsic rewards. What Can You Do To Maintain Or Increase Intrinsic Motivation? If a reward is viewed as informing athletes about their ability in a positive manner, then the rewards will likely foster internal satisfaction and intrinsic motivation. The extrinsic reward is given for a behavior that is already intrinsically rewarding.Įxtrinsic rewards can also be used to maintain or strengthen intrinsic motivation.
 The extrinsic reward is not directly connected to a specific behavior or performance level. (e.g., there is only one reward and I didn’t get it) The extrinsic reward provides negative information about the athlete’s ability. The extrinsic reward controls the behaviors of the athlete (e.g., I’m playing to keep my college scholarship). Under the following situations, it is likely that extrinsic rewards will weaken intrinsic motivation. Desire to learn new skills or strategiesĮxtrinsic Rewards: Weakening or Strengthening Intrinsic Motivationīased on the two types of extrinsic motivation, extrinsic rewards may weaken or strengthen the intrinsic motivation of athletes. Greater interest, enjoyment, and effort towards achievement. Behaviors (Similar to intrinsic motivation). Choice to participate even with extrinsic rewards. Less interest, value, and effort towards achievement. These two major types of extrinsic motivation are highlighted here.īehavior controlled by the extrinsic rewards On the other hand, athletes may continue to feel like they control their own behavior even with the presence of extrinsic rewards. An over-emphasis on extrinsic motivation may lead athletes to feel like their behavior is controlled by the extrinsic rewards. Extrinsically motivated athletes tend to focus on the competitive or performance outcome. Fewer changes (ups and downs) in motivationĮxtrinsic motivation may come from social sources, such as not wanting to disappoint a parent, or material rewards, such as trophies and college scholarships. Intrinsically motivated athletes participate in sport for internal reasons, particularly pure enjoyment and satisfaction, and intrinsically motivated athletes typically concentrate on skill improvement and growth.īehaviors Related to Intrinsic Motivation As a coach, you can help increase or maintain the intrinsic motivation of college athletes even with the presence of extrinsic rewards, such as scholarships. However, athletes in highly competitive levels of sport may experience decreases in their intrinsic motivation because of the increasing use of extrinsic rewards offered by the media, coaches, and parents. Extrinsic rewards, when used correctly, can be beneficial to athletes. Athletes who are intrinsically motivated participate in sports for internal reasons, such as enjoyment, whereas athletes who are extrinsically motivated participate in sports for external reasons, such as material rewards.Įxtrinsic rewards are central to competitive sports athletes receive publicity, awards, and money, among other things, and college level athletes obtain scholarships for their talents. These reasons fall into the two major categories of intrinsic and extrinsic motivation. University of Northern Iowa, Cedar Falls, IAĪthletes compete in and practice sport for a variety of reasons.
The extrinsic reward is not directly connected to a specific behavior or performance level. (e.g., there is only one reward and I didn’t get it) The extrinsic reward provides negative information about the athlete’s ability. The extrinsic reward controls the behaviors of the athlete (e.g., I’m playing to keep my college scholarship). Under the following situations, it is likely that extrinsic rewards will weaken intrinsic motivation. Desire to learn new skills or strategiesĮxtrinsic Rewards: Weakening or Strengthening Intrinsic Motivationīased on the two types of extrinsic motivation, extrinsic rewards may weaken or strengthen the intrinsic motivation of athletes. Greater interest, enjoyment, and effort towards achievement. Behaviors (Similar to intrinsic motivation). Choice to participate even with extrinsic rewards. Less interest, value, and effort towards achievement. These two major types of extrinsic motivation are highlighted here.īehavior controlled by the extrinsic rewards On the other hand, athletes may continue to feel like they control their own behavior even with the presence of extrinsic rewards. An over-emphasis on extrinsic motivation may lead athletes to feel like their behavior is controlled by the extrinsic rewards. Extrinsically motivated athletes tend to focus on the competitive or performance outcome. Fewer changes (ups and downs) in motivationĮxtrinsic motivation may come from social sources, such as not wanting to disappoint a parent, or material rewards, such as trophies and college scholarships. Intrinsically motivated athletes participate in sport for internal reasons, particularly pure enjoyment and satisfaction, and intrinsically motivated athletes typically concentrate on skill improvement and growth.īehaviors Related to Intrinsic Motivation As a coach, you can help increase or maintain the intrinsic motivation of college athletes even with the presence of extrinsic rewards, such as scholarships. However, athletes in highly competitive levels of sport may experience decreases in their intrinsic motivation because of the increasing use of extrinsic rewards offered by the media, coaches, and parents. Extrinsic rewards, when used correctly, can be beneficial to athletes. Athletes who are intrinsically motivated participate in sports for internal reasons, such as enjoyment, whereas athletes who are extrinsically motivated participate in sports for external reasons, such as material rewards.Įxtrinsic rewards are central to competitive sports athletes receive publicity, awards, and money, among other things, and college level athletes obtain scholarships for their talents. These reasons fall into the two major categories of intrinsic and extrinsic motivation. University of Northern Iowa, Cedar Falls, IAĪthletes compete in and practice sport for a variety of reasons. 
Stephanie Hatch, Danielle Thomsen, Jennifer J.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
